While comprehensive study resources are listed in the subsequent sections, this guide focuses on strategic insights derived from practical experience rather than serving as a generic preparation manual.
My preparation methodology involved a comparative assessment of multiple learning platforms, ranging from A Cloud Guru and Cloud Academy to the legacy Linux Academy platform and Coursera’s official high-level overview. Additionally, I participated in an intensive corporate training program characterized by its accelerated pace. To optimize the study process, I evaluated available mobile tools and technical literature, identifying the most effective resources detailed below, including Dan Sullivan’s comprehensive guide.
The certification process required a rigorous two-month regimen, consisting of 2–4 hours of daily study alongside full-time dedication on weekends. This preparation was underpinned by over three years of hands-on GCP architecture experience and a previously obtained Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer certification.
I successfully passed the online proctored exam on the first attempt.
Strategic Solutions to Sample Case Studies
The case studies are accessible on the official exam website. During the examination, you will encounter all three scenarios presented in a split-screen format. Questions related to these case studies constitute approximately 30% of the total exam content.
Note: The objective is not to memorize the text of the case studies but to understand the architectural patterns and solutions associated with them.
Mountkirk Games
| Requirement | Solution |
| Serve multi-regional instance group backends. | Global HTTP Load Balancer. |
| Multi-regional ingest and storage. | Pub/Sub combined with Datastore, BigQuery, or Cloud Storage depending on data structure. |
| Monitoring infrastructure. | Google Cloud Operations Suite (formerly Stackdriver) metrics can drive Google Compute Engine (GCE) group autoscaling. |
| Handling slow or late data. | Pub/Sub for scaling and buffering, followed by Dataflow for processing, windowing, and arranging late data. |
| Latency reduction for global user base. | Multi-regional GCE managed instance groups, HTTP Load Balancer, and multi-region Datastore. |
| Scaling strategy. | Autoscaling managed instance groups (running hardened Linux distributions). Scaling is driven by Cloud Operations metrics and the HTTP Load Balancer. |
| User profiles and game state storage. | NoSQL transactional database (Datastore). |
| Game activity storage. | Time-series database. Use Bigtable if millisecond response time is required; otherwise, BigQuery. |
| SQL queries on historical data exceeding 10TB. | BigQuery. |
| Processing files uploaded by mobile devices. | Upload to Cloud Storage, then process via Dataflow pipeline. |
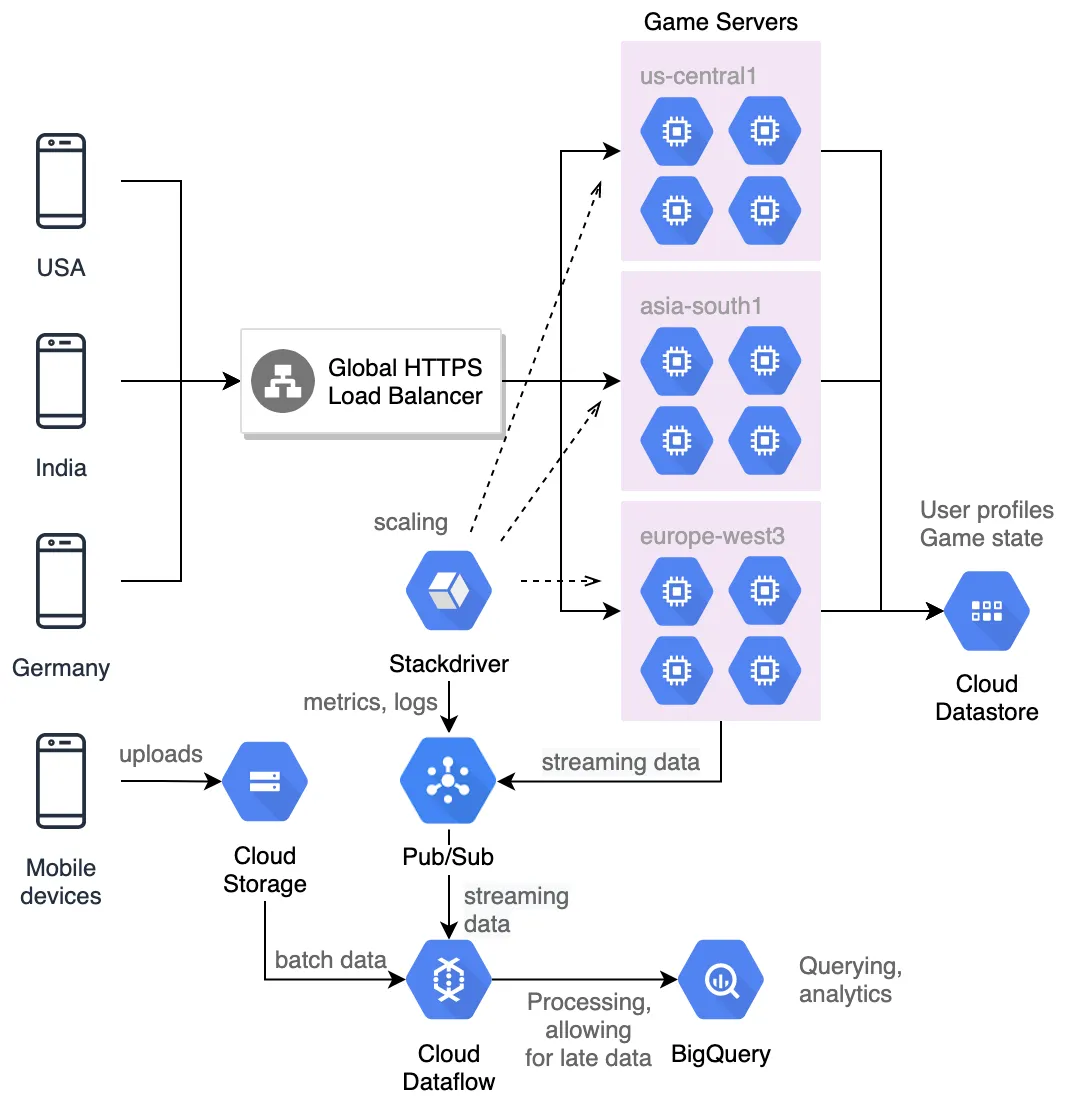
Dress4Win
| Requirement | Solution |
| Migration methodology. | Migrate data first, build a prototype, then migrate the applications. |
| Deployment automation. | Utilize gcloud for automated management scripts, Cloud Deployment Manager, Terraform, or other Infrastructure as Code (IaaC) tools. |
| CI/CD for hybrid environments. | Jenkins, Spinnaker, or Cloud Build. |
| High Availability and Failover support. | Replicate the environment on Google Cloud, replicate MySQL to Cloud SQL, and utilize DNS cutover strategies for application servers. |
| Encryption in transit and at rest. | Customer-supplied encryption keys (CSEK). Keys are Base64-encoded, uploaded to a private Cloud Storage bucket, and used as gsutil parameters during data access. |
| Private connectivity between data center and cloud (Option A). | Cloud VPN. Supports up to 8 tunnels (3 Gbps each). Suitable for aggregate bandwidth ≤ 3 Gbps. Uses IPsec/IKE. Note: No SLA and data traverses the public internet. High Availability requires HA Cloud VPN configuration. |
| Private connectivity between data center and cloud (Option B). | Cloud Interconnect. Dedicated Interconnect provides direct physical connections (up to 80 Gbps, ≥99.9% SLA). Partner Interconnect utilizes service providers (up to 10 Gbps, ≥99.9% SLA). Maintains RFC 1918 IP space. |
| Database Migration (MySQL). | Lift and shift to Cloud SQL (native support). Strategy: Create a read replica managed by Cloud SQL, sync with on-premises instance, point applications to the replica, and promote it to a standalone instance. |
| Redis 3 Server migration. | Deploy Redis on Compute Engine or export to Memorystore for Redis. |
| Web application servers migration. | Autoscaled GCE managed instance groups with custom machine types, or re-architect for Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) / App Engine. |
| Hadoop/Spark migration. | Cloud Dataproc connected to Cloud Storage. |
| Messaging queue (RabbitMQ) migration. | Replace with Pub/Sub or deploy RabbitMQ on a GCE managed instance group. |
| Auxiliary services (Jenkins, monitoring, bastion hosts). | Lift and shift to GCE instances using custom machine types. |
| Storage migration (iSCSI/SAN). | Migrate to GCE persistent disks configured in a SAN cluster. |
| NAS (images, logs, backups). | Migrate to Cloud Storage or Filestore. |
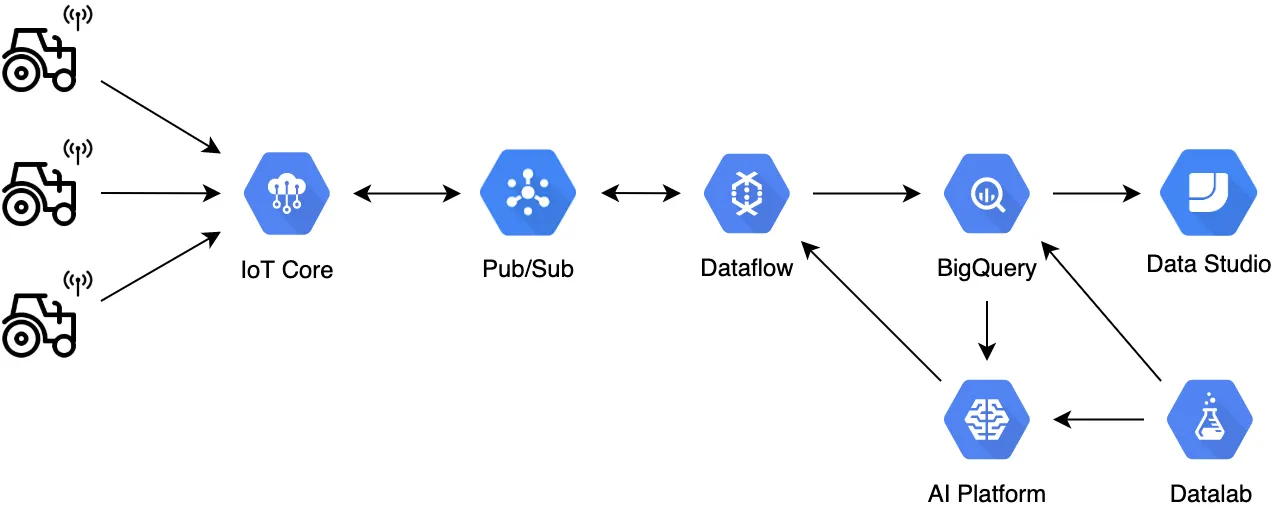
TerramEarth
| Requirement | Solution |
| Connectivity Optimization. | Convert to 100% cellular data where possible to decrease unplanned vehicle downtime to less than one week. |
| Ingestion Management. | Cloud IoT Core with built-in managed security. |
| API Management. | Cloud Endpoints to manage and protect APIs. |
| Global Data Ingestion. | Pub/Sub to ingest data from cellular devices globally. |
| Data Processing pipeline. | Dataflow processes streaming data from Pub/Sub and inserts it into BigQuery. Alternatively, stage data in Cloud Storage, clean with Dataprep, and process via Dataflow into BigQuery. |
| Predictive Analytics. | Vertex AI (formerly Cloud ML Engine) utilizes data from BigQuery to predict customer needs and breakdowns, optimizing parameters for deployment back to devices. |
| Analytics Visualization. | Looker Studio (formerly Data Studio) for dashboards shared with dealers and for creating partnership offers. |
| Advanced Analytics. | Datalab or Vertex AI Workbench for visual notebooks working with BigQuery and ML data. |
| Expansion Strategy. | Utilize multi-regional and global services. |
| Backup Strategy. | Regular exports from BigQuery to Cloud Storage. |
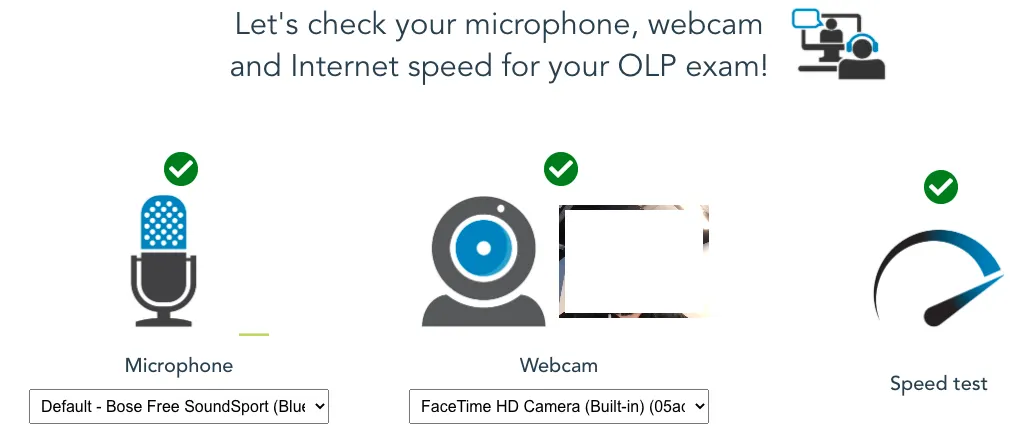
Online Proctored Exam: Procedural Guidelines
The certification is available via both onsite testing centers and online proctoring. Based on the online experience, the following protocols and recommendations are critical:
- Pre-exam preparation requires creating a Webassessor Biometric Profile and installing the Sentinel application with necessary permissions (camera, microphone).
- System stability is paramount. Perform a system test well in advance. Ensure all checks are green; any red flags can lead to immediate failure or inability to launch the exam.
- Identity verification requires two forms of government-issued photo ID (e.g., passport, driver’s license) where the face and full name are clearly visible. Documents with expiration dates are recommended over those without.
- The exam environment must be strictly controlled. The proctor will monitor you continuously via webcam and microphone for the full duration. The desk must be clear, no smartwatches or additional screens are permitted, and no other individuals may be present.
- Handwritten notes are prohibited. An integrated whiteboard within the Sentinel app is provided for comments and calculations.
- You must remain at your desk for the entire duration. Breaks are not permitted, so plan accordingly.
- The dedicated desktop application locks the screen. Closing this window manually may be interpreted as an exam submission. In case of technical issues (freezes or errors), contact support immediately rather than attempting to troubleshoot by closing the app.
- Support teams are generally responsive. Do not hesitate to contact them regarding any issues before, during, or after the session.
Recommended Preparation Resources
Web Resources
- Legacy Linux Academy Lucidchart: Highly recommended for architectural visualization.
- Official GCP Sample Questions: Essential for validating knowledge readiness 24 hours prior to the exam.
- Official GCP Exam Roadmap: Useful for planning and identifying knowledge gaps.
- Coursera – Preparing for the Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect Exam: Excellent for a high-level overview and understanding the logic behind question resolution, though insufficient as a standalone study source.
- Community Question Banks (e.g., Examtopics): Useful for practice, but requires critical thinking as community-provided answers may vary in accuracy. Always verify reasoning against documentation.
- GCP Free Tier: Essential for hands-on practice (includes $300 credit).
Mobile Resources
Mobile applications facilitate continuous learning during commute or downtime.
- Android Test Prep for Google Professional Cloud Architect (Magic Bytes Soft): Rated highly for content relevance.
- Legacy Learning Platform Apps: Useful for reviewing flashcards and key concepts on the go.
Selected Literature
- Official Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Architect Study Guide by Dan Sullivan: This resource covers 100% of the exam objectives and includes relevant quizzes. It is widely considered the definitive text for this certification.
FAQ
What is the primary motivation for this certification?
For professionals, the certification validates expertise for career advancement and market positioning. For organizations, maintaining a specific number of certified architects is often a requirement for partnership tiers with Google Cloud, ensuring a steady stream of enterprise projects.
Is the exam useful for Developers/Engineers?
No. It does not focus on implementation details or “how-to” usage of services. It focuses on selecting the appropriate tools for specific business requirements.
Is the exam useful for Architects?
Yes. It validates the ability to assess trade-offs and select optimal tools. The case studies serve as reusable architectural patterns.
What is the typical preparation time?
Approximately 1–2 months, assuming a schedule of 2–3 hours per working day and dedicated study on weekends.
Is the exam difficult?
Yes, it is considered rigorous.
Summary and Key Takeaways
- Historical platforms like Linux Academy set a high standard for preparation.
- Current platforms vary in quality; critical assessment of their content is necessary.
- Coursera’s preparation course provides a necessary high-level overview. Pay close attention to how instructors dissect questions – this logic is crucial for the exam.
- Analyze Google’s official sample questions deeply. Understand the rationale behind both correct and incorrect options.
- Hands-on experience is a prerequisite. A background of 2+ years is strongly recommended.
- Expert-led corporate training may vary in effectiveness depending on the instructor’s practical experience.
- Memorize the solutions for the case studies (Mountkirk Games, Dress4Win, TerramEarth), not the case text itself.
- Schedule the exam in advance. High demand often results in a lack of available slots for 2–3 weeks out.


